India has long been a significant player in the global trade ecosystem, exporting everything from textiles to technology. Recently, the government introduced a transformative initiative to boost India’s export potential further. By turning districts across the country into specialized export hubs, this initiative aims to strengthen the nation’s trade capabilities. Moreover, it is an integral part of the larger “Aatmanirbhar Bharat” vision and is closely aligned with the “Make in India” and “Vocal for Local” movements. Ultimately, the goal is to transform India into a global manufacturing and exporting powerhouse by unlocking the untapped potential of its districts.
The Concept Behind Districts as Export Hubs
The Districts as Export Hubs (DEH) initiative aims to promote local industries by identifying the unique products and services from different districts that have the potential for global markets. Specialized export hubs are being developed in these districts, leveraging their inherent strengths—agricultural, artisanal, or industrial.

Each district boasts unique products that represent centuries of craftsmanship, local resources, and specialized industrial capacities. For instance, Moradabad is renowned for its brassware, Bhadohi for its carpets, and Ludhiana for its hosiery and textiles. Thus, by focusing on these regions and their speciality products, the DEH initiative aims to boost both exports and the local economies. In this way, the initiative leverages regional strengths to enhance India’s overall trade performance.
The District as Export Hubs initiative seeks to achieve this by:
- Identifying export-worthy products.
- Encouraging local manufacturers and businesses to scale up production to meet international demand.
- Providing infrastructure and logistical support.
- Offering guidance and training to meet global standards of production and quality.

Strategic Objectives of the District as Export Hubs Initiative
The strategic objectives of the DEH initiative are multi-fold, and they reflect the broader trade and economic goals of India:
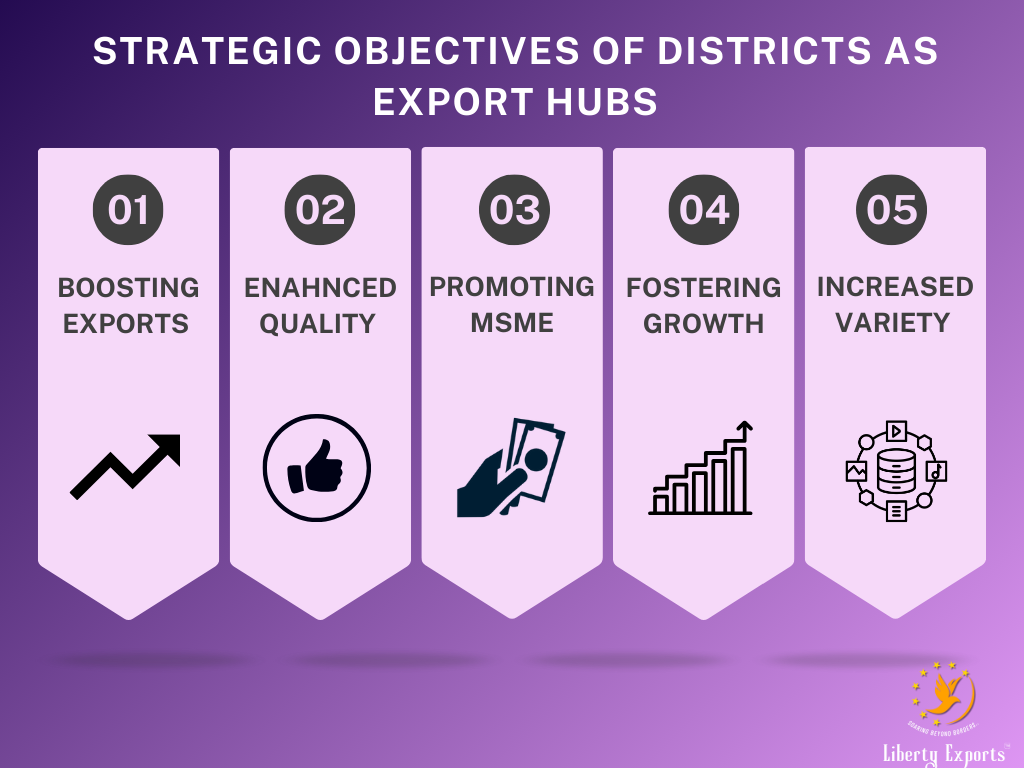
- Boosting Exports: One of the primary objectives is to increase the export of district-specific products. Thus, by focusing on products that are already part of the local economy, the government aims to leverage existing strengths rather than creating entirely new industries.
- Enhancing Competitiveness: To compete in the global market, Indian products must meet international standards in terms of quality, packaging, and marketing. The DEH initiative provides technical know-how, access to finance, and support to upgrade infrastructure. This ensures that Indian products can compete with the best in the world.
- Promoting MSMEs: A significant portion of district-specific industries involves small and medium enterprises (MSMEs). These businesses form the backbone of India’s economy, however, face many challenges in accessing larger markets. The DEH initiative focuses on integrating MSMEs into the export ecosystem, providing them with a platform to grow.
- Fostering Inclusive Growth: At the district level, the initiative promotes exports, spreading economic growth to underdeveloped regions. This creates job opportunities in rural and semi-urban areas, fostering more balanced regional development.
- Diversifying Export Baskets: A few sectors, including IT services, textiles, and pharmaceuticals, have accounted for the majority of India’s exports. The DEH initiative aims to diversify the export basket by promoting a wider variety of products from different regions.
Key Components of the Districts as Export Hubs Initiative
The DEH initiative is a comprehensive approach that covers various aspects of trade and industry. The key components include:
- District Export Action Plans: Each district is required to prepare a detailed action plan, which outlines the steps necessary to promote the identified products for export. This includes mapping out the entire value chain, identifying gaps, and setting up the infrastructure needed to meet international demand.
- Capacity Building and Skill Development: The initiative recognizes that many local manufacturers may not have experience in exporting. To address this, training programs are being organized to enhance skills related to production techniques, quality control, packaging, and marketing.
- Quality Assurance and Standards: Exporting products requires adherence to international standards. The government is helping local industries obtain certifications and comply with regulations to ensure their products can meet the requirements of foreign markets.
- Logistics and Infrastructure Support: A key challenge in promoting district-level exports is the lack of adequate infrastructure. The DEH initiative focuses on improving logistics by building export warehouses, cold chains, and transportation networks that can handle the increased volume of goods.
- Financial Support and Incentives: To encourage local industries to participate in the export initiative, the government is providing financial support through subsidies, tax breaks, and easier access to credit. This makes it easier for small businesses to scale up their operations and invest in modern technology.
- Promotional Activities: The government is also organizing trade fairs, exhibitions, and buyer-seller meets, both domestically and internationally, to showcase the products from different districts. These events help local manufacturers network with potential buyers from around the world.
Success Stories: Early Wins
The Districts as Export Hubs initiative has already seen success in several districts across the country. For example, the carpet industry in Bhadohi has experienced a significant rise in exports as a result of the support provided under this program. Likewise, Moradabad’s brassware has gained increased traction in international markets, leading to a surge in orders from countries such as the U.S. and Europe. In addition, these districts are now becoming more competitive on the global stage.
In Gujarat, the district of Surat, known for its diamond-cutting and polishing industry, has benefited from streamlined processes and greater access to international buyers. This has boosted exports and helped the local economy grow.
Challenges and the Way Forward
Although the DEH initiative holds great promise, it is not without challenges. One of the key issues is ensuring that infrastructure development keeps pace with the growing needs of the export hubs. Without efficient transportation networks, warehousing, and cold chain systems, moving products quickly to global markets will be difficult.
Furthermore, local manufacturers must consistently meet international standards, which requires sustained efforts in capacity building and quality control. In addition, market access remains a concern, especially for smaller businesses that may struggle to compete with larger, more established exporters.
Nevertheless, with the government’s focus on addressing these challenges, the future of the DEH initiative appears promising. By turning districts into specialized export hubs, India can unlock the economic potential of its regions, create new job opportunities, and strengthen its position in the global trade ecosystem.
Conclusion
The Districts as Export Hubs initiative is a bold step towards making India a key player in global trade. By harnessing the unique strengths of its districts, the initiative not only boosts exports but also fosters inclusive, sustainable growth. With the right infrastructure, support, and strategic vision, India’s districts could become the next engines of its export-led growth story.
This blog post provides an overview of the current trends and challenges in India’s agricultural export landscape. Stay updated on our website Liberty Exports for more insights on the latest developments in Indian agriculture and trade.


